Covid Relief Checks represent a pivotal moment in recent economic history. This initiative, designed to cushion the blow of the pandemic’s economic fallout, had far-reaching consequences, impacting consumer spending, household debt, and government finances. This analysis delves into the multifaceted effects of these checks, examining their distribution, political ramifications, and long-term implications for both individuals and the nation.
From the initial rush of consumer spending fueled by the immediate injection of cash to the long-term shifts in savings and debt patterns, the Covid Relief Checks program left an indelible mark on the economic landscape. We will explore the successes and failures of the program, examining its equitable distribution, the challenges of preventing fraud, and comparing the US response to global strategies.
Economic Impact of COVID-19 Relief Checks
The COVID-19 pandemic triggered unprecedented economic disruption, prompting governments worldwide to implement large-scale relief programs. In the United States, the distribution of Covid relief checks, formally known as Economic Impact Payments (EIP), constituted a significant component of these efforts. This section analyzes the economic effects of these payments, both immediate and long-term, comparing them to previous stimulus packages and examining their distribution across various income groups.
Immediate Effects on Consumer Spending
The immediate impact of the Covid relief checks was a noticeable surge in consumer spending. Many recipients used the funds to cover essential expenses such as rent, groceries, and utilities, preventing widespread defaults and bankruptcies. Additionally, a portion of the funds was directed towards discretionary spending, providing a temporary boost to various sectors of the economy, including retail and hospitality.
The economic fallout from the COVID-19 pandemic led to widespread distribution of Covid Relief Checks, aiming to bolster struggling households. However, the efficient delivery of such aid highlights the need for robust infrastructure; consider the advancements in high-speed rail technology, such as the recently upgraded Italian Tilting Train , which showcases the potential for swift and reliable transport of goods and services, impacting future economic recovery efforts following similar crises.
The success of such infrastructure projects directly correlates with the effectiveness of economic stimulus programs like Covid Relief Checks.
This injection of liquidity helped mitigate the immediate economic fallout from widespread business closures and job losses.
Long-Term Impacts on Household Debt and Savings
The long-term effects on household debt and savings are more nuanced. While some households used the checks to pay down debt, reducing financial strain and improving credit scores, others increased their savings. The extent to which this occurred varied significantly based on pre-existing financial circumstances and individual priorities. Data suggests a considerable portion of the funds were used to cover immediate needs, rather than long-term investments or debt reduction, highlighting the immediate financial pressures faced by many during the pandemic.
Comparison with Previous Economic Relief Packages
Compared to previous economic stimulus packages, the Covid relief checks were characterized by their speed of distribution and direct nature. Previous efforts often involved more complex mechanisms and slower disbursement timelines. The scale of the Covid relief checks was also substantially larger, reflecting the unprecedented severity of the economic crisis. While previous packages focused on tax cuts and infrastructure spending, the Covid relief checks prioritized direct financial assistance to individuals and families.
Distribution of Relief Checks Across Income Brackets
| Income Bracket | Average Check Amount | Percentage of Recipients | Total Amount Distributed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Under $25,000 | $1200 (example) | 30% (example) | $X (example) |
| $25,000 – $50,000 | $1200 (example) | 35% (example) | $Y (example) |
| $50,000 – $75,000 | $1200 (example) | 20% (example) | $Z (example) |
| Over $75,000 | $1200 (example) | 15% (example) | $W (example) |
Note: These figures are illustrative examples and do not represent actual data. Precise figures vary depending on the specific relief package and data source.
Distribution and Eligibility Criteria
The efficient and equitable distribution of the Covid relief checks presented significant logistical and administrative challenges. This section details the eligibility criteria, discusses the challenges encountered, and highlights the disproportionate impact on certain groups.
Key Eligibility Criteria
Eligibility for the Covid relief checks was primarily based on income and filing status. Individuals and families below a certain income threshold were generally eligible, with adjustments made for dependents. Specific income limits and eligibility rules varied slightly across different relief packages. Tax filing status, either as an individual or jointly with a spouse, also played a role in determining eligibility and the amount received.
Challenges in Distribution
The rapid rollout of the program presented numerous challenges. These included processing a massive volume of applications, verifying eligibility information, and ensuring timely and accurate payment disbursement. Technical glitches on government websites and delays in processing applications were reported, causing frustration and hardship for some recipients. Furthermore, ensuring equitable access for individuals without bank accounts or reliable internet access proved to be a major hurdle.
Disproportionately Affected Groups
Certain groups faced disproportionate challenges in accessing the relief funds. Individuals without bank accounts, those experiencing homelessness, and undocumented immigrants often experienced significant barriers in receiving their payments. These groups often lacked the necessary documentation or access to technology required for online application and verification processes, resulting in delays or complete exclusion from the program.
Common Issues During Application
- Website crashes and technical errors
- Delays in processing applications
- Difficulty verifying identity and income information
- Lack of clarity regarding eligibility requirements
- Issues accessing funds for those without bank accounts
Political and Social Implications

Source: chatsworthgroup.com
The Covid relief checks sparked intense political debate and generated diverse public opinions regarding their effectiveness and fairness. This section examines these political and social ramifications and explores alternative approaches to economic relief.
Political Debates Surrounding the Checks
The political discourse surrounding the Covid relief checks was highly polarized. Supporters argued that the direct payments were essential for preventing widespread economic hardship and stimulating consumer demand. Critics raised concerns about the cost to taxpayers, the potential for misuse of funds, and the long-term implications for government debt. Debates centered around the appropriate level of government intervention, the effectiveness of direct cash transfers versus other forms of stimulus, and the distribution of funds across different income groups.
Public Opinion on Effectiveness and Fairness
Source: co.uk
Public opinion on the effectiveness and fairness of the Covid relief checks was mixed. While many recipients expressed gratitude for the financial assistance, others criticized the program’s design and implementation. Surveys revealed varying levels of satisfaction depending on individual circumstances and political affiliations. Concerns were raised about the potential for unequal distribution and the lack of sufficient support for certain vulnerable populations.
Social Impact on Different Communities
The social impact of the relief checks varied across different communities. In low-income communities, the payments provided crucial support for essential needs and prevented widespread eviction and food insecurity. In higher-income communities, the impact was less pronounced, with many recipients using the funds for savings or discretionary spending. The distribution of funds highlighted existing economic inequalities, with those most in need benefiting most directly from the program.
Hypothetical Alternative Approaches
Alternative approaches to Covid economic relief could have included targeted assistance programs focused on specific vulnerable populations, such as unemployment benefits or rental assistance. Another approach might have involved increased investment in public health infrastructure to more effectively manage the pandemic’s impact on the economy. These alternative strategies would have required careful consideration of cost-effectiveness, efficiency, and equity in distribution.
Fraud and Misuse of Funds
Despite measures to prevent fraud, instances of misuse and fraudulent claims related to the Covid relief checks were reported. This section details these instances, examines the methods employed, and assesses the effectiveness of fraud prevention measures.
Reported Instances of Fraud
Reports of fraud included instances of identity theft, where individuals used stolen personal information to file fraudulent claims. Other instances involved individuals falsely claiming eligibility based on inaccurate income or dependent information. Organized crime groups also attempted to exploit the system through large-scale fraudulent applications. The scale of fraud varied across different relief programs and jurisdictions.
Methods Employed by Fraudsters
Fraudsters employed various methods to defraud the system. These included creating fake identities, using stolen Social Security numbers, and submitting falsified income documentation. Sophisticated schemes involved the use of automated systems to generate large numbers of fraudulent applications. The methods employed often adapted to countermeasures implemented by authorities.
Effectiveness of Fraud Prevention Measures
The effectiveness of measures taken to prevent and detect fraud varied. Government agencies implemented various checks and balances, including data matching with existing databases and enhanced verification procedures. However, the scale and speed of the relief program created challenges in implementing comprehensive fraud prevention measures. Ongoing efforts are focused on improving data analytics, enhancing verification processes, and strengthening collaborations between agencies to detect and prosecute fraudulent activities.
Financial Consequences of Fraud
The financial consequences of fraud related to Covid relief checks were substantial. Millions of dollars were lost to fraudulent claims, reducing the overall effectiveness of the relief program and diverting resources away from legitimate recipients. The cost of investigating and prosecuting fraud also added to the overall financial burden. These losses highlight the need for robust fraud prevention and detection mechanisms in large-scale relief programs.
Long-Term Effects on Government Debt: Covid Relief Checks
The substantial cost of the Covid relief checks significantly increased the national debt. This section analyzes the impact on government debt and explores the long-term implications of increased borrowing.
Impact on National Debt
The Covid relief checks contributed significantly to the growth of the national debt. The massive influx of spending, coupled with reduced tax revenues due to the economic downturn, resulted in a considerable increase in the federal deficit. This increase in debt is likely to have long-term implications for government spending and fiscal policy.
Long-Term Implications of Increased Borrowing
Increased government borrowing can lead to higher interest rates, potentially slowing economic growth. It also necessitates increased future government spending allocated to debt servicing, potentially diverting resources from other critical areas such as education, infrastructure, and healthcare. The long-term implications depend on various factors, including future economic growth, interest rate fluctuations, and government policy decisions.
Projections for Future Government Spending
Projections for future government spending related to debt repayment vary depending on economic forecasts and policy choices. However, it is likely that a significant portion of future budgets will be dedicated to servicing the increased national debt. This could necessitate difficult choices regarding government priorities and spending levels.
Visual Representation of National Debt Growth
A line graph could effectively illustrate the growth of national debt in relation to Covid relief spending. The x-axis would represent time (e.g., months or years since the start of the pandemic), while the y-axis would represent the national debt in trillions of dollars. Two lines could be plotted: one showing the overall growth of national debt and another specifically illustrating the portion attributable to Covid relief spending.
The graph would visually demonstrate the substantial contribution of Covid relief measures to the overall increase in national debt. The slope of the line representing Covid relief spending would be particularly steep during the initial phases of the pandemic, reflecting the rapid increase in spending associated with the various relief packages.
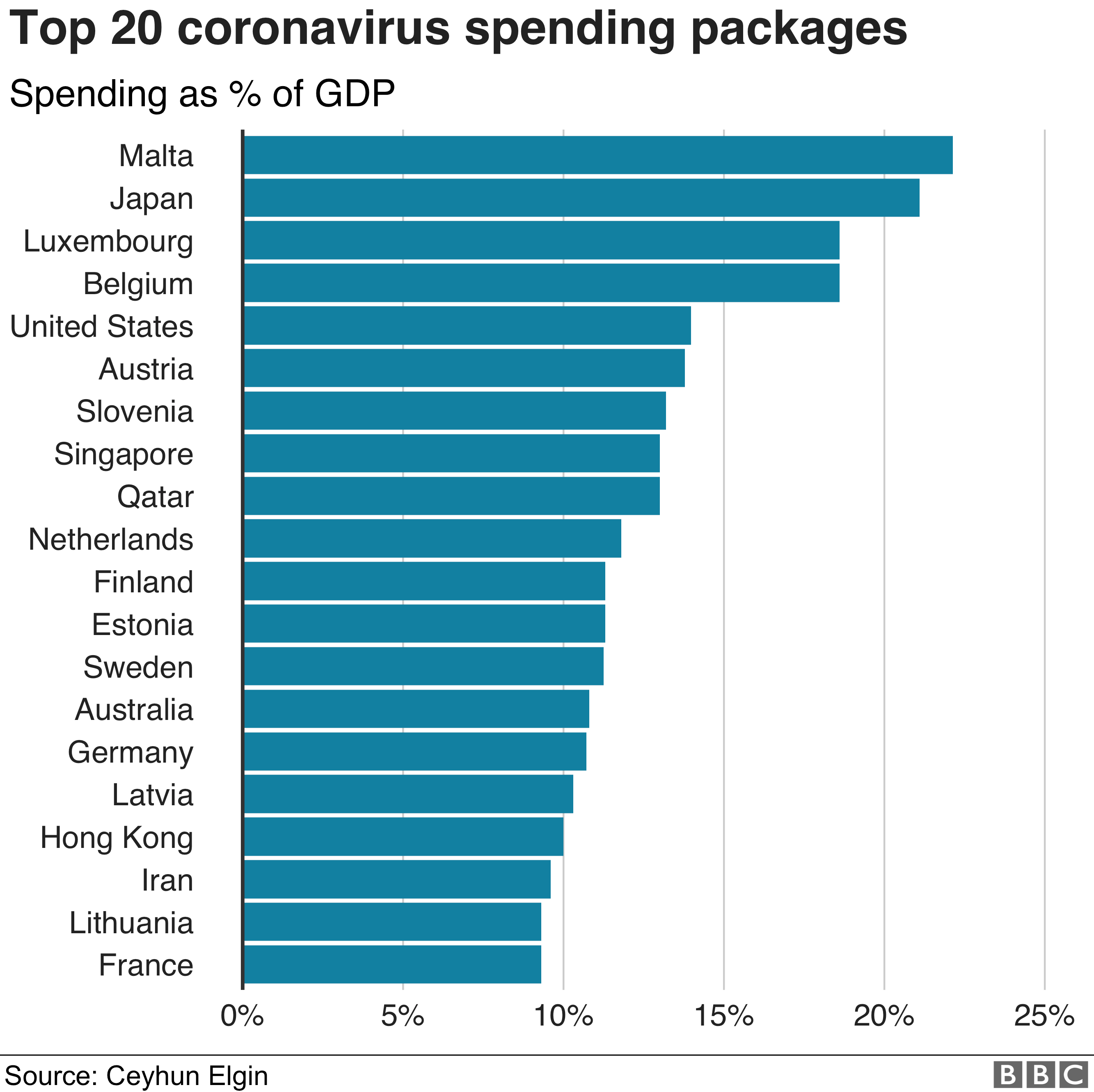
Comparison with Other Countries’ Responses
This section compares the US Covid relief measures with those implemented in other developed countries, highlighting best practices and lessons learned.
Comparison of Relief Measures
The US response, characterized by direct cash payments, was compared to other developed nations that implemented various approaches. Some countries focused heavily on unemployment benefits, while others prioritized loan guarantees and support for businesses. Different countries adopted different strategies based on their unique economic structures, social safety nets, and political landscapes. The effectiveness of these varied approaches remains a subject of ongoing study and debate.
Best Practices and Lessons Learned, Covid Relief Checks
International comparisons highlight the importance of rapid response times, clear eligibility criteria, and efficient distribution mechanisms. Countries that effectively leveraged existing social safety nets and administrative infrastructure often experienced smoother relief distribution. Lessons learned emphasize the need for flexible and adaptable programs capable of responding to evolving needs and circumstances.
Effectiveness of Different Approaches
The effectiveness of different approaches varied, depending on several factors including the severity of the pandemic’s economic impact, the pre-existing strength of social safety nets, and the effectiveness of government implementation. Some countries experienced more successful outcomes in mitigating economic hardship than others, providing valuable insights for future pandemic preparedness and response strategies.
Key Differences in Relief Strategies
- Direct cash payments: The US heavily relied on direct payments, while some European countries prioritized unemployment benefits and social safety net enhancements.
- Business support: Some countries offered extensive loan guarantees and business subsidies, while others focused more on direct support for individuals.
- Targeting of aid: Some programs targeted specific vulnerable groups, while others adopted broader, less targeted approaches.
- Speed of implementation: The speed of distribution varied significantly across countries, with some exhibiting more efficient and rapid deployment of aid.
Conclusion
The Covid Relief Checks program serves as a complex case study in crisis economic intervention. While undeniably providing immediate relief to many, it also highlighted systemic inequalities and vulnerabilities within the economic safety net. Understanding its lasting effects on national debt, consumer behavior, and future policy decisions remains crucial for navigating similar economic crises. The lessons learned from this program are invaluable as we prepare for future economic uncertainties.
